半人馬座A 目录 型態(組織) 超新星 距離 鄰近的星系和星系集團的資料 業餘天文學的資訊 图片 相關條目 外部連結 參考資料 导航菜单SEDS: Peculiar Galaxy NGC 5128ESA/Hubble images of Centaurus ANASA's APOD: The Galaxy Within Centaurus A (3/4/06)NASA's APOD: X-Rays from an Active Galaxy (7/5/03)High-resolution image of Centaurus ACentaurus ANGC5128 Centaurus ADSS2SDSSGALEXIRAS氢αX射线天文照片天图文章和图片Hubble Provides Multiple Views of How to Feed a Black HoleCentaurus A JetNASA/IPAC Extragalactic DatabaseThe SBF Survey of Galaxy Distances. IV. SBF Magnitudes, Colors, and Distancesdoi:10.1086/318301Centaurus A - NGC 5128doi:10.1007/s001590050011Bibcode:1966ApJS...14....1Adoi:10.1086/190147Bibcode:1954ApJ...119..215Bdoi:10.1086/145813Bibcode:1983AJ.....88..296Hdoi:10.1086/113318NASA/IPAC Extragalactic DatabaseBibcode:1986IAUC.4208....1EBibcode:1987PASP...99..592Pdoi:10.1086/132020Bibcode:2007ApJ...654..186FarXiv:astro-ph/0605707doi:10.1086/506612Bibcode:2010AcA....60..121MarXiv:1006.2458Bibcode:2010PASA...27..457HarXiv:0911.3180doi:10.1071/AS09061Bibcode:2004A&A...413..903RarXiv:astro-ph/0310639doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20034031Bibcode:2009AcA....59..403MarXiv:0909.0181Bibcode:2010PASA...27..475HarXiv:1004.4907doi:10.1071/AS09063New distances to galaxies in the Centaurus A groupdoi:10.1051/0004-6361:20020042Groups of galaxies within 80 Mpc. II - The catalogue of groups and group membersGeneral study of group membership. II - Determination of nearby groupsThe Local Group and Other Neighboring Galaxy Groupsdoi:10.1086/426368Firestorm of Star Birth in Galaxy Centaurus ARadio Galaxy编
C1C2C3C4C5C6C7C8C9C10C11C12C13C14C15C16C17C18C19C20C21C22C23C24C25C26C27C28C29C30C31C32C33C34C35C36C37C38C39C40C41C42C43C44C45C46C47C48C49C50C51C52C53C54C55C56C57C58C59C60C61C62C63C64C65C66C67C68C69C70C71C72C73C74C75C76C77C78C79C80C81C82C83C84C85C86C87C88C89C90C91C92C93C94C95C96C97C98C99C100C101C102C103C104C105C106C107C108C109
透鏡狀星系特殊星系電波星系星暴星系半人馬座A/M83星系團半人馬座NGC天體PGC天體阿普天體科德韦尔天体
半人馬座透鏡星系活躍星系核相對論性噴流超大質量黑洞X射線無線電波光速星爆星系史匹哲太空望遠鏡特殊星系透鏡星系橢圓星系約翰·赫歇爾赫頓·阿普合併恆星形成超新星SN 1986G艾文思Ia超新星聯星系統熱失控秒差距經典造父變星米拉變星第二型造父變星本星系群米拉變星行星狀星雲半人馬座 A/M83星系集團星系集團M83南風車星系半人馬座ω球狀星團ALMAMPG/ESO 2.2-meter telescopeLa Silla ObservatoryHubble Space TelescopeNASAESA史匹哲太空望遠鏡Chandra X-rayrelativistic jetblack holeFalse-colourradioinfraredkeVX-raysynchrotron emissionthermal radiation
body.skin-minerva .mw-parser-output table.infobox captiontext-align:center
| 半人馬座 A | |
|---|---|
 半人馬座 A (NGC 5128) | |
| 觀測資料 (J2000 曆元) | |
| 星座 | 半人馬座 |
| 赤經 | 13h 25m 27.6s[1] |
| 赤緯 | -43° 01′ 09″[1] |
| 紅移 | 547 ± 5 公里/秒[1] |
| 距離 | 1千3百70萬 ± 90萬光年 (420 ± 30萬秒差距)[2] |
| 類型 | S0 pec[1] |
視大小 (V) | 25′.7 × 20′.0[1] |
視星等 (V) | 7.8[1] |
| 值得注意的特徵 | 異常的塵埃帶 |
| 其他名稱 | |
NGC 5128,[1]Arp 153,[1]PGC 46957[1] | |
參見:星系、星系列表 | |
半人馬座A,也稱為NGC 5128,是位於半人馬座內距離大約1千4百萬光年遠的一個透鏡星系。它是最靠近地球的電波源之一,也是被專業天文學家廣泛研究的活躍星系核[3]。這個星系也是全天第五亮的星系,所以即使這個星系只能在南半球和北半球的低緯度地區看見,它依然也還是業餘天文學家的理想目標[4]。
相對論性噴流的能量被相信是從在星系核心的超大質量黑洞附近的空間喷射出來的,輻射出X射線和無線電波的波長。以十年的間隔對噴流的電波進行觀察,天文學家確定噴流內側部分的移動速度達到光速的一半。X射線則是噴流內的高能微粒在更遠處與周圍的氣體碰撞所產生的。
如同對其他的星爆星系所做的觀測,碰撞導致恆星的形成和引發強烈的爆炸。使用史匹哲太空望遠鏡,科學家證實了半人馬座 A是經由一個大型橢圓星系與一個小螺旋星系碰撞的結果。
目录
1 型態(組織)
2 超新星
3 距離
4 鄰近的星系和星系集團的資料
5 業餘天文學的資訊
6 图片
7 相關條目
8 外部連結
9 參考資料
型態(組織)
半人馬座A在型態學上可能是特殊星系,因為從地球上觀察,這個細看起來像是透鏡星系或橢圓星系疊加上一條塵埃帶[5]。這個特殊的星系在1847年首度被約翰·赫歇爾確認,並被收錄在赫頓·阿普的《特殊星系圖集》(1966年出版),作為"受攝"星系和塵埃吸收的最佳範例之一[6]。這個星系的奇怪型態被公認為是兩個較小星系合併的結果[7]。
這個星系的核球主要由演化中的紅色恆星組成[5];然而,塵埃盤是最近的恆星形成的場所[3],已經確認的恆星形成區超過100個[8]。
超新星
在半人馬座A曾經檢測到一顆超新星[9]。
這顆超新星,SN 1986G,是艾文思於1986年在塵埃帶內發現的[10],
稍後被鑑定是一顆Ia超新星[11]。Ia超新星通常是有一顆白矮星的聯星系統,白矮星由伴星攫取氣體,使質量至足以點燃在核心的碳融合反應,引發熱失控的核融合。SN 1986G被用來演示Ia超新星的光譜並不是全都一樣,Ia超新星的光譜可能會隨著時間的推移,在亮度和形式上有不同的改變[11]。
2016年2月发现第二颗超新星SN2016adj,稍后经被鉴定为是一颗Ⅱb超新星。
距離
自1980年代以來,估計NGC 5128的距離通常在3-5百萬秒差距[2][12][13][14][15][16]。發現在NGC 5128的經典造父變星受到濃厚的塵埃巷道遮蔽,依據消光法的本質和考慮其他的因素,距離估計在300-350萬秒差距[13][14]。在NGC 5128也發現米拉變星[16]和第二型造父變星[13][14],而後者很少在本星系群之外被發現[17]。以一些米拉變星和行星狀星雲測定的距離,認為是更遠的〜380萬秒差距[18][15]。
鄰近的星系和星系集團的資料
半人馬座 A位於半人馬座 A/M83星系集團的兩個子集團中的一個的中心位置,是一個鄰近的星系集團[19]。M83 (南風車星系)在另一個集團的中心,有時這兩個集團會被視為一個集團[20][21],有時又會被視為兩個集團[22]。然而,環繞著半人馬座 A的星系和環繞著M83實際上是非常接近的,且這兩個集團之間有著相互的運動[23]。
業餘天文學的資訊
半人馬座 A位於半人馬座ω (一個肉眼可見的球狀星團) 北方約4°的地方[4]。因為這個星系有著高表面亮度和相對較大的視角,他是業餘天文觀測的理想目標。明亮的核球和黑色的塵埃帶在找星鏡和大的雙筒望遠鏡中就能見到[4],而其他的結構要更大的望遠鏡才能看見[4]。
图片

半人馬座A的光晕

The radio galaxy Centaurus A, as seen by ALMA

Image taken by the Wide Field Imager attached to the MPG/ESO 2.2-meter telescope at the La Silla Observatory.

"Hubble's panchromatic vision... reveals the vibrant glow of young, blue star clusters..."[24]

A Hubble Space Telescope (HST) image of the dust disk in front of the nucleus of Centaurus A. Credit: HST/NASA/ESA.

This image of the central parts of Centaurus A reveals the parallelogram-shaped remains of a smaller galaxy that was absorbed about 200 to 700 million years ago.

史匹哲太空望遠鏡的完整盤面影像

Chandra X-ray view of Cen A in X-rays showing one relativistic jet from the central black hole

 播放媒体
播放媒体
Video about Centaurus A jets.
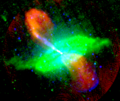
"False-colour image of the nearby radio galaxy Centaurus A, showing radio (red), 24-micrometre infrared (green) and 0.5-5 keV X-ray emission (blue). The jet can be seen to emit synchrotron emission in all three wavebands. The lobes only emit in the radio frequency range, and so appear red. Gas and dust in the galaxy emits thermal radiation in the infrared. Thermal X-ray radiation from hot gas and non-thermal emission from relativistic electrons can be seen in the blue 'shells' around the lobes, particularly to the south (bottom)."[25]
相關條目
M87 - 也是強烈電波源的巨大橢圓星系。
NGC 1316 - 也是強烈電波源的相似透鏡星系。
外部連結
SEDS: Peculiar Galaxy NGC 5128- ESA/Hubble images of Centaurus A
NASA's APOD: The Galaxy Within Centaurus A (3/4/06)
NASA's APOD: X-Rays from an Active Galaxy (7/5/03)
High-resolution image of Centaurus A showing the discrete elements of galactic core
Centaurus A at UniverseToday.com- NGC5128 Centaurus A
WikiSky上关于半人馬座A的内容:DSS2, SDSS, GALEX, IRAS, 氢α, X射线, 天文照片, 天图, 文章和图片
參考資料
- STScI. Hubble Provides Multiple Views of How to Feed a Black Hole. Press release: Space Telescope Science Institute. March 14, 1998.
- Chandra X-Ray Observatory Photo Album Centaurus A Jet
^ 1.01.11.21.31.41.51.61.71.8 NASA/IPAC Extragalactic Database. Results for Centaurus A. [2006-12-06].
^ 2.02.1 J. L. Tonry, A. Dressler, J. P. Blakeslee, E. A. Ajhar, A. B. Fletcher, G. A. Luppino, M. R. Metzger, C. B. Moore. The SBF Survey of Galaxy Distances. IV. SBF Magnitudes, Colors, and Distances. Astrophysical Journal. 2001, 546 (2): 681–693. doi:10.1086/318301.
^ 3.03.1 F. P. Israel. Centaurus A - NGC 5128. Astronomy and Astrophysics Review. 1998, 8: 237–278. doi:10.1007/s001590050011.
^ 4.04.14.24.3 D. J. Eicher. The Universe from Your Backyard. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. 1988. ISBN 0-521-36299-7.
^ 5.05.1 A. Sandage; J. Bedke. Carnegie Atlas of Galaxies. Washington, D.C.: Carnegie Institution of Washington. 1994. ISBN 0-87279-667-1.
^ H. Arp. Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies. Astrophysical Journal Supplement. 1966, 14: 1–20. Bibcode:1966ApJS...14....1A. doi:10.1086/190147.
^ W. Baade; R. Minkowski. On the Identification of Radio Sources. Astrophysical Journal. 1954, 119: 215–231. Bibcode:1954ApJ...119..215B. doi:10.1086/145813.
^ P. W. Hodge; R. C. Kennicutt Jr. An atlas of H II regions in 125 galaxies. Astrophysical Journal. 1982, 88: 296–328. Bibcode:1983AJ.....88..296H. doi:10.1086/113318.
^ NASA/IPAC Extragalactic Database. Results for extended name search on Centaurus A. [2007-03-07].
^ R. Evans; R. H. McNaught; C. Humphries. Supernova 1986G in NGC 5128. IAU Circular. 1986, 4208: 1. Bibcode:1986IAUC.4208....1E.
^ 11.011.1 M. M. Phillips; A. C. Phillips; S. R. Heathcote; V. M. Blanco; 等. The type 1a supernova 1986G in NGC 5128 – Optical photometry and spectra. Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific. 1987, 99: 592–605. Bibcode:1987PASP...99..592P. doi:10.1086/132020.
^ 引用错误:没有为名为ned-dist的参考文献提供内容
^ 13.013.113.2 Ferrarese Laura; Mould Jeremy R.; Stetson Peter B.; Tonry John L.; 等. The Discovery of Cepheids and a Distance to NGC 5128. The Astrophysical Journal. 2007, 654: 186. Bibcode:2007ApJ...654..186F. arXiv:astro-ph/0605707. doi:10.1086/506612.
^ 14.014.114.2 Majaess, D. The Cepheids of Centaurus A (NGC 5128) and Implications for H0. Acta Astronomica. 2010, 60: 121. Bibcode:2010AcA....60..121M. arXiv:1006.2458.
^ 15.015.1 Harris, Gretchen L. H.; Rejkuba, Marina; Harris, William E. The Distance to NGC 5128 (Centaurus A). Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia. 2010, 27 (4): 457–462. Bibcode:2010PASA...27..457H. arXiv:0911.3180. doi:10.1071/AS09061.
^ 16.016.1 Rejkuba, M. The distance to the giant elliptical galaxy NGC 5128. Astronomy and Astrophysics. 2004, 413 (3): 903. Bibcode:2004A&A...413..903R. arXiv:astro-ph/0310639. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20034031.
^ Majaess, D.; Turner, D.; Lane, D. Type II Cepheids as Extragalactic Distance Candles. Acta Astronomica. 2009, 59: 403. Bibcode:2009AcA....59..403M. arXiv:0909.0181.
^ Harris, Gretchen L. H. NGC 5128: The Giant Beneath. Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia. 2010, 27 (4): 475. Bibcode:2010PASA...27..475H. arXiv:1004.4907. doi:10.1071/AS09063.
^ I. D. Karachentsev, M. E. Sharina, A. E. Dolphin, E. K. Grebel, D. Geisler, P. Guhathakurta, P. W. Hodge, V. E. Karachetseva, A. Sarajedini, P. Seitzer. New distances to galaxies in the Centaurus A group. Astronomy and Astrophysics. 2002, 385: 21–31. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20020042.
^ R. B. Tully. Nearby Galaxies Catalog. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. 1988. ISBN 0-521-35299-1.
^ P. Fouque, E. Gourgoulhon, P. Chamaraux, G. Paturel. Groups of galaxies within 80 Mpc. II - The catalogue of groups and group members. Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement. 1992, 93: 211–233.
^ A. Garcia. General study of group membership. II - Determination of nearby groups. Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement. 1993, 100: 47–90.
^ I. D. Karachentsev. The Local Group and Other Neighboring Galaxy Groups. Astronomical Journal. 2005, 129: 178–188. doi:10.1086/426368.
^ Firestorm of Star Birth in Galaxy Centaurus A. NASA. [27 September 2012].
^ Radio Galaxy. English Wikipedia. Wikimedia Foundation. [25 November 2012].
| |||||||||||||||||











